The language of humiliation is a step towards a second civil war, argues RAMZY BAROUD
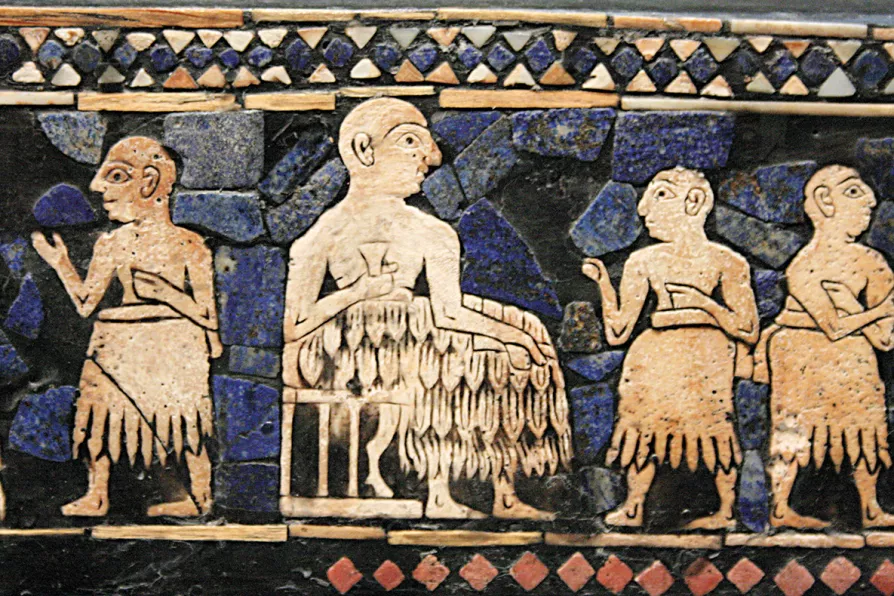

 A 2600BC depiction of a king in Sumer, an early human civilisation in the fertile crescent where humans had adapted to eat starchy foods through farming
[Michel Wal/Creative Commons]
A 2600BC depiction of a king in Sumer, an early human civilisation in the fertile crescent where humans had adapted to eat starchy foods through farming
[Michel Wal/Creative Commons]
THE taste of food is something that seems fundamental. In Marx’s view, expressed in A Contribution to the Critique of Political Economy (1859), a physical property like taste provides a measure of the use-value of a commodity as distinct from its exchange-value: “From the taste of wheat, it is not possible to tell who produced it, a Russian serf, a French peasant or an English capitalist.”
Today, humanity consumes nearly 800 million metric tons of wheat a year. Other foods such as potatoes, rice, and different cereal crops are essential to diets around the world.
All of these contain large amounts of carbohydrates in the form of starch molecules. These molecules were made by the plants as an energy store. When plants photosynthesise, they use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into glucose molecules.
New research into mutations in sperm helps us better understand why they occur, while debunking a few myths in the process, write ROX MIDDLETON, LIAM SHAW and MIRIAM GAUNTLETT

Olive oil remains a vital foundation of food, agriculture and society, storing power in the bonds of solidarity. Though Palestinians are under attack, they continue to press forward write ROX MIDDLETON, LIAM SHAW and MIRIAM GAUNTLETT

JOHN GREEN wades through a pessimistic prophesy that does not consider the need for radical change in political and social structures










